Machine
Common word to refer to participants’ bikes.
Manifold
This is the part that contains the ducts coming in and out of the cylinder head, depending on whether we’re talking about the inlet or exhaust manifold, directing gases to or from their respective cylinders. The shape, size, and internal design are of great importance to achieve maximum engine performance.
Marshal(s)
The staff of GPs. They can have many duties. There are technical marshals, timing marshals, track marshals (the ones we see at track posts, etc.)
Their work, depending on the position, may involve ensuring that the rules are upheld, or that quick and efficient action is taken in the event of an accident.


Medical car
This is the car we can see going around the circuit before sessions during a GP weekend. Its mission is mainly to perform a reconnaissance of the track before a session and take the medical team to the site quickly if a rider suffers an accident on the track.
Mph
Miles per hour. Speed measurement unit in the Imperial system. It is mainly used in the US and England. It’s equivalent to 1.62 km/h, 0.86 Kn, or 0.44 m/s. MotoGP speeds are commonly expressed in mph as well as km/h.
m/s
Metres per second. Speed measurement unit in the international system. In the world of motorsports, this measurement may be used to express the average speed of pistons inside the engine, for example. Outside this environment, it’s commonly used to measure the speed of projectiles. It’s equivalent to 3.6 km/h, 2.23 mph, or 1.94 m/s.
mmHg
Millimetres of mercury. This is a manometric pressure unit based on the use of mercury. It doesn’t belong to the international system, but we can usually find it in blood pressure monitors or vacuum gauges in mechanics. It’s equivalent to 0.00133 bar, 0.019 Psi, 0.00131 Atm, or 0.00135 Kg/cm2
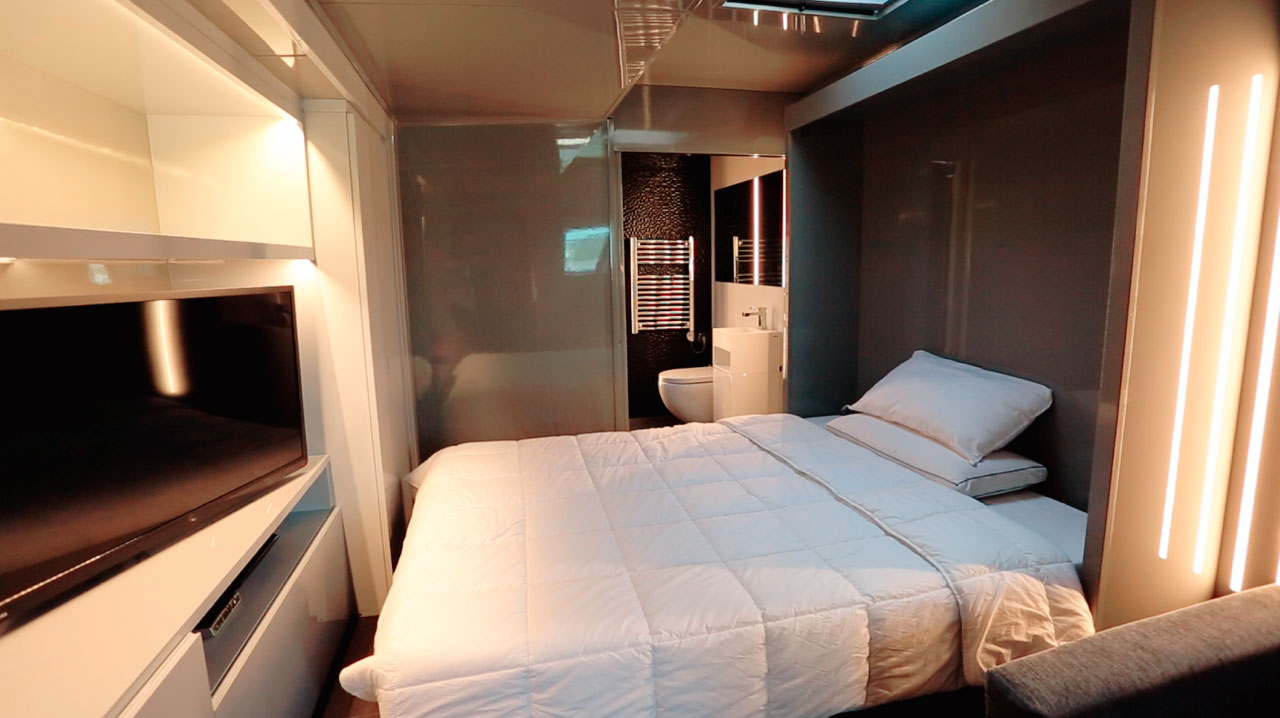


Motorhome
Vehicles used by teams, whether caravans or trailers, to sleep at night, carry materials, or work.
Neutral
A gearbox is in neutral when no movement is transferred to the transmission, even with the clutch deactivated. MotoGP bikes with a seamless gearbox have a neutral position but, to place it in this position, riders need to operate a specific lever.
Nm
Newton metre. Unit used to measure the momentum or torque in the international system (momentum or torque produced by a force exerted at a certain distance). It is usually seen in engine data or in screw tightening torques. It’s equivalent to 0.1 kg/m or 0.737 lb/ft.
With this information and the number of revolutions per minute, we can calculate the power of an engine.
Oil filter
This is the filter responsible for removing any impurities in the lubricant.
Oil pump
This part is responsible for providing appropriate oil pressure to the engine to ensure it is correctly lubricated at any rotation speed.
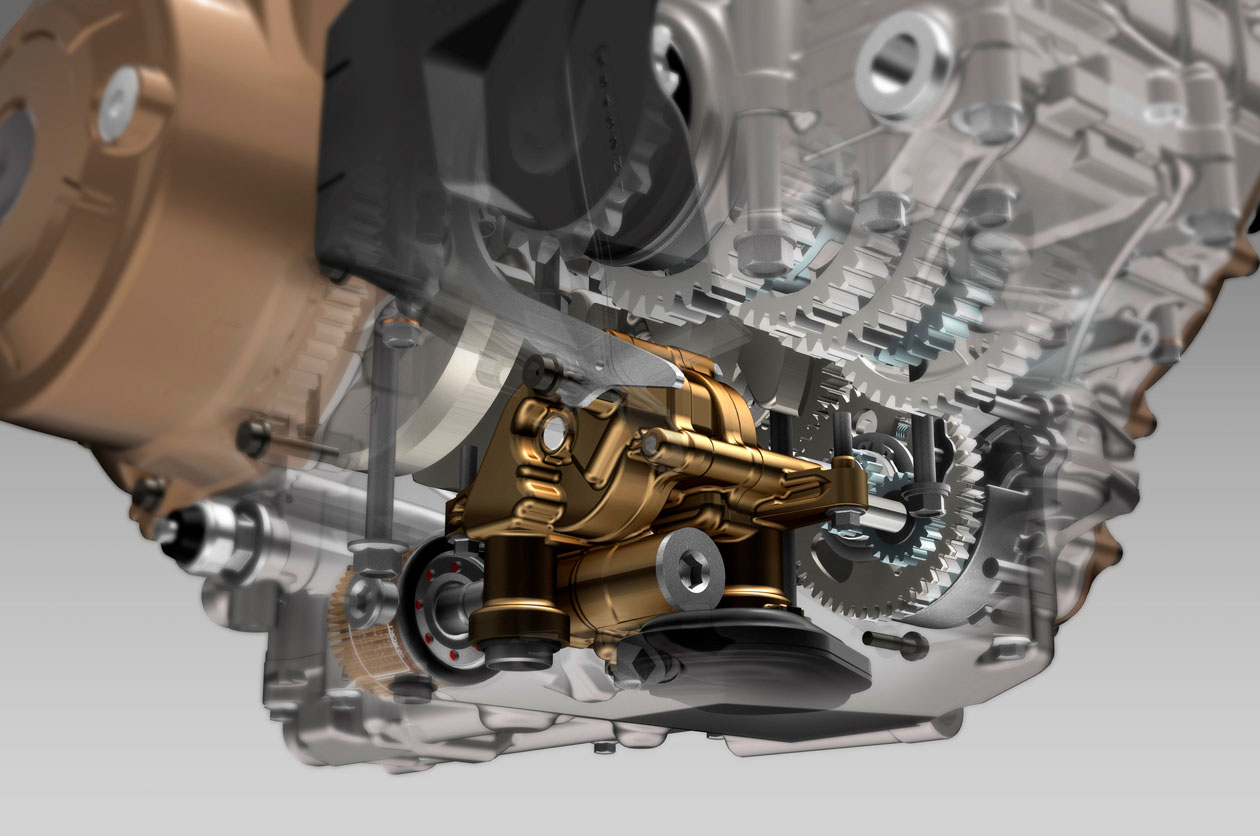

Oil sump
Located at the bottom part of the engine, this is where oil is stored or where it falls after going through the engine. There are vehicles with dry oil sumps that store oil in specific tanks.
OHV
Over Head Valve. This is a type of engine with a camshaft in the engine block. It is no longer widely used. They use a rod system to operate the valves in the cylinder head.
Official(s)
Common word to refer to Marshal(s)
Onboard
Refers mainly to TV cameras mounted on the bikes.
Overtake
Manoeuvre in which one rider overtakes another.


Paddock
This is the area where the teams park the motorhomes and where we can find other members of the team. It is on the opposite side of the pitlane to the boxes. We can usually see riders walking around this place, as well as mechanics moving around tyres or other bike parts.
Paddock stand
These are the elements used to hold the bike vertically when it’s not moving, making it possible to change tyres, fit heaters, etc.
Parc Fermé
This is the place in the pitlane where the three riders that have gained a spot on the podium stop their bikes and are interviewed immediately after the race.
Pass
Different term for “overtake”.
Pit board
These are the structures where teams put plates to display data, such as times, laps, and rivals, to tell their rider this information when they drive over the finish line. Today, this information is also communicated through the bike’s instrument panel, on the virtual pit board.
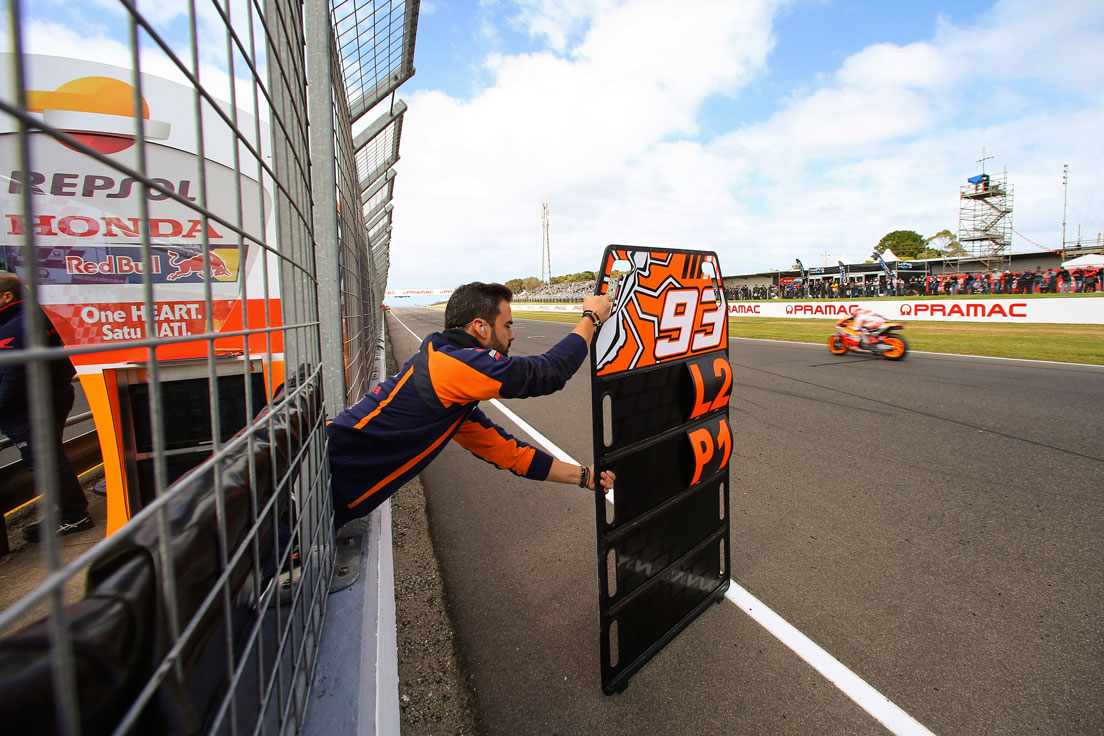


Pit crew
These are the mechanics and assistants in the pitlane, either to help out during a bike change or simply to put it in the pit. In MotoGP, there can only be five mechanics in the pit crew during a session.
Pitlane
This is the area where you can enter and exit the track circuit. The pits are on one side and the pit wall is on the other. In this lane, speed in MotoGP is limited to 60 km/h and riders have to use a limiter to avoid being fined.
Pit limiter
This is a special program in the bike’s electronics that gets activated when the corresponding button is pushed, limiting the maximum speed of the bike while going through the pitlane.
Pit Stop
A Pit Stop refers to when a rider goes into the pitlane and stops in front of its pit to fix the bike, change wheels, make adjustments, or perform another task depending on the type of competition. In MotoGP it is common for riders to make a pit stop during qualifying sessions.
Pit Wall
This is the area between the pitlane and the finish line where the teams mount the monitors to monitor the development of the race and where the pit boards are prepared.
Podium
Place where the top three riders stand after the race. This also represents the achievement of taking one of the top three spots in a sporting event.


Pole Position
This is the first position on the grid given to the rider with the best time during the qualifying ride. In MotoGP, Marc Márquez is the greatest poleman in history, which means he is the rider who’s achieved the most pole positions in his career.
Practice
Practice is when riders train to learn a new course or to simulate a race, for example. Also, during a GP weekend, riders have four free practice sessions, FP1, FP2, FP3, and FP4.
Puncture
When a tyre is punctured by a foreign body and loses air pressure.
PSI
Pounds per square inch. This is a manometric pressure measurement unit used mainly in the US and the UK. We can usually see this in tyre inflators. It’s equivalent to 0.069 Bar, 0.068 Atm, 0.07 Kg/cm2, or 51.71 mmHg.
MotoGP Glossary: G to L
MotoGP Glossary: Q to S
2 months ago


 Join Us
Join Us  Join Us
Join Us 

